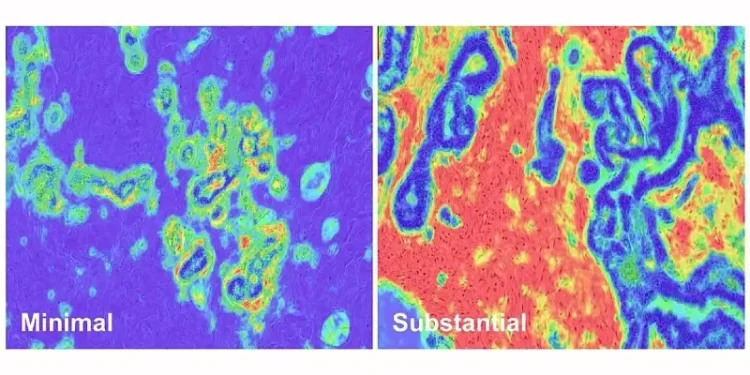
NIH researchers have uncovered a subtle yet critical tissue change—stromal disruption—that may signal a higher risk of aggressive breast cancer and poor survival rates.
This breakthrough could transform early detection and care, particularly for women with benign breast conditions.
Early Warning Signs Hidden in Breast Tissue
In a groundbreaking study published on May 14, 2025, researchers at the National Cancer Institute (NCI)—part of the NIH—identified a tissue biomarker that may help predict the development of aggressive breast cancer.
Using advanced machine learning, the team analyzed over 9,000 breast tissue samples to uncover a phenomenon called stromal disruption, where changes in connective tissue structure were closely tied to cancer severity and outcomes.
What Is Stromal Disruption?
Stromal tissue supports and surrounds breast cells. The study found that when this tissue becomes disordered or inflamed, it may signal the body’s shift toward cancer development. This process is now being labeled stromal disruption.
The researchers believe stromal disruption could function as a cost-effective, scalable biomarker—especially useful in low-resource settings. It could help clinicians identify women who are at risk even before cancer becomes invasive.
How the Study Was Conducted
The research analyzed three groups of tissue samples:
-
4,023 from healthy women
-
974 with benign breast disease
-
4,223 from women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer
Machine learning algorithms were used to detect structural changes that are hard to spot with the naked eye. These digital tools allowed for precise analysis across thousands of samples.
Findings at a Glance
Disruption Signals at All Stages
| Tissue Type | Stromal Disruption Linked to… | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy Tissue | Shared risk traits (age, obesity, etc.) | Suggests early biological pathway |
| Benign Breast Disease | Higher cancer risk, faster onset | Potential early detection marker |
| Invasive Breast Cancer | Poorer survival, especially ER+ subtypes | Prognostic marker for treatment |
These findings indicate that stromal changes may occur well before cancer develops, offering a new window for preventive care.
Risk Factors Associated with Disruption
The study also revealed that women with the following traits were more likely to show stromal disruption:
-
Black ethnicity, higher BMI, or multiple childbirths
-
Family history of breast cancer
-
Younger age at tissue donation
These associations suggest a common biological pathway that could link risk factors to aggressive cancer outcomes via stromal tissue changes.
Why This Matters for Diagnosis and Prevention
One of the most promising aspects of stromal disruption is its accessibility. Unlike genetic testing or molecular diagnostics, identifying this biomarker doesn’t require costly equipment.
This opens the door to wider adoption, especially in clinics with limited resources.
Potential Benefits:
-
Affordable screening for high-risk individuals
-
Earlier interventions before cancer spreads
-
Improved risk stratification for patients with benign findings
What’s Next in Research?
Lead researcher Dr. Mustapha Abubakar of the Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics emphasized the need for further studies.
The team is now exploring whether anti-inflammatory treatments or lifestyle changes might reduce stromal disruption—and in turn, lower cancer risk.
“Understanding how inflammation and wound healing contribute to these changes may unlock new prevention strategies,”
said Dr. Abubakar.
Final Thoughts
This discovery represents a significant step toward identifying and preventing aggressive forms of breast cancer. Stromal disruption could become a new tool in the clinician’s kit—simple to detect, widely available, and predictive of serious disease.
Want to learn more?
Explore the full findings in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute (May 14, 2025 edition), or visit cancer.gov for more on the latest breast cancer research.
Sources: National Institutes of Health.
Prepared by Ivan Alexander Golden, Founder of THX News™, an independent news organization delivering timely insights from global official sources. Combines AI-analyzed research with human-edited accuracy and context.