On June 18, 2025, the United States sanctioned five senior leaders of the Cártel Jalisco Nueva Generación (CJNG), including notorious kingpin Rubén Oseguera Cervantes, also known as “El Mencho.”
The move, which formally designates them as Specially Designated Global Terrorists, marks a pivotal escalation in the U.S. strategy to disrupt international drug trafficking networks and curb fentanyl-related deaths.
A Turning Point in the U.S. Fight Against Cartels
The CJNG, widely considered one of the world’s most dangerous criminal organizations, has now been labeled a Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO) and its main figures placed on the Specially Designated Global Terrorist (SDGT) list.
These designations activate far-reaching legal tools that allow U.S. agencies to freeze assets, disrupt funding channels, and ban American entities from engaging in any transactions with CJNG-linked individuals or groups.
This latest enforcement action builds upon a multi-year campaign targeting the cartel’s drug production, money laundering, and international expansion.
Who Was Sanctioned and Why It Matters
The new sanctions directly target five influential CJNG figures:
-
Rubén “El Mencho” Oseguera Cervantes – CJNG leader and most-wanted cartel figure globally
-
Audias Flores Silva – Oversees cartel drug labs producing meth and fentanyl
-
Unnamed CJNG Commander – Linked to the high-profile murder of a Mexican influencer
-
Two Additional Leaders – Integral in coordinating trafficking routes and financial operations
The U.S. Department of State also announced reward offers of up to $15 million for information leading to El Mencho’s arrest and up to $5 million for Flores.
This development underscores the CJNG’s reach and the escalating U.S. response to its role in fueling America’s opioid crisis.
Why CJNG’s Terrorist Designation Changes the Landscape
Legal and Financial Consequences
Labeling a cartel as a terrorist group enables U.S. authorities to:
-
Freeze domestic and international assets
-
Criminalize material support to the organization
-
Strengthen coordination with global financial systems
This classification positions the CJNG alongside groups like al-Qaeda and ISIS, reflecting how deeply U.S. policy now views cartel violence and fentanyl trafficking as threats to national security.
CJNG’s Global Footprint: From Mexico to India
The CJNG has evolved beyond a regional criminal enterprise.
Its operations now span three continents, with drug manufacturing and trafficking hubs in:
-
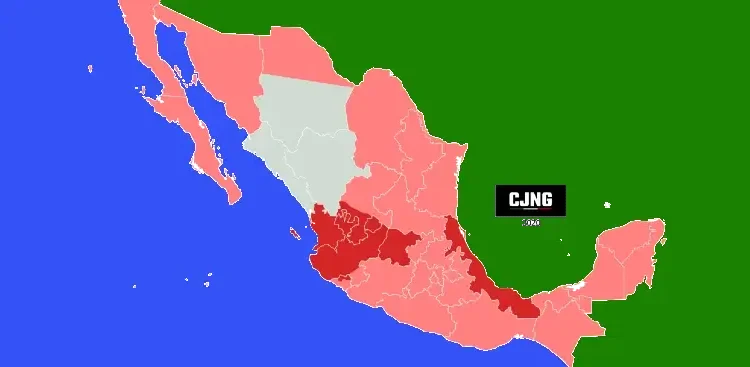
Mexico – Home base with strongholds in Jalisco, Michoacán, and Veracruz
-
United States – Distribution networks in Arizona, California, Texas, and Midwest cities
-
India – Recently uncovered meth production site in Uttar Pradesh
-
Guatemala – Expansion into southern Mexico’s border region
The cartel has also increased its activities in human trafficking, extortion, and fuel theft, creating multi-dimensional threats across borders.
CJNG Activity Timeline (2020–2025)
| Year | Event or Development | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Operation Python: 600+ CJNG arrests in U.S. | Major disruption of cartel networks |
| 2021 | CJNG expands to Chiapas & Guatemala | Regional power shift in southern Mexico |
| 2022 | Arrest of “La Jefa,” El Mencho’s wife | Blow to financial operations |
| 2024 | CJNG-linked meth lab found in India | Proof of international expansion |
| 2025 | CJNG leaders designated terrorists | Elevated global response to cartel violence |
CJNG’s Violence and Influence on Daily Life
The cartel’s reputation is grounded in brutal tactics—kidnappings, executions, public ambushes, and social media intimidation.
The recent assassination of a Mexican influencer during a livestreamed event exemplifies its growing use of terror to dominate public spaces and suppress dissent.
This violence doesn’t stop at the Mexican border.
U.S. communities are suffering the consequences through:
-
Increased fentanyl-related overdoses
-
Gang violence linked to CJNG distribution cells
-
Economic burdens on healthcare and law enforcement
Strategic Impact and Public Health Implications
CJNG remains a top contributor to the U.S. fentanyl crisis. Fentanyl is now the leading cause of death for Americans aged 18 to 49, according to the CDC.
By targeting the cartel’s leadership, the U.S. hopes to:
-
Reduce the flow of fentanyl into American cities
-
Disrupt financial gains fueling violence
-
Encourage public cooperation with law enforcement (via reward programs)
Takeaways
-
The U.S. now categorizes CJNG leaders as global terrorists.
-
Sanctions block access to financial systems and expand legal tools.
-
This action builds on years of anti-cartel efforts and international cooperation.
-
CJNG remains a multi-threat organization, active across three continents.
-
The campaign aims to reduce drug supply, cartel violence, and deaths linked to opioids.
International Pressure and Community Vigilance
The United States has intensified its efforts, but defeating a network as agile as CJNG requires sustained pressure, international collaboration, and community involvement.
These sanctions signal a strong pivot—but long-term outcomes depend on continued vigilance, public awareness, and multinational engagement.
Stay informed on the evolving global strategies used to counter cartel threats and track how these actions affect local safety, public health, and international relations.
Sources: US Department of State, DEA, Wikipedia, The Soufan Center, US Treasury, The White House and Council on Foreign Relations.
Prepared by Ivan Alexander Golden, Founder of THX News™, an independent news organization delivering timely insights from global official sources. Combines AI-analyzed research with human-edited accuracy and context.